With Covid-19, the world has turned digital overnight, with businesses increasing their “digital” dimension to adapt rapidly to a new reality based on the e-commerce boom, the coexistence of physical and digital channels or omnichannel retailing to reach consumers regardless of their location. The companies’ adoption of automation and digitization, embodied by remote work, increased the demand for IT specialists and developers with technical expertise in areas like telemedicine, telework, online communication, cybersecurity, and data analytics.
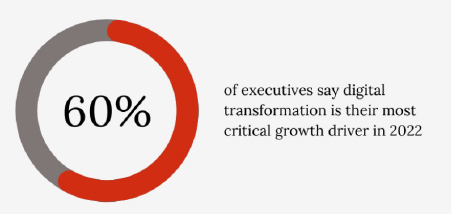
Before we knew it, business leaders were forced to adapt to the unexpected, and the accelerated digital transformation trend led them to rethink their IT strategy. For many CEOs, this moment can represent the first steps toward defining their corporate purpose in a deliberate way. Project areas that change managers or controllers should pay particular attention to include the following:
- Keeping up with the shift in technological trends, ensuring the performance of software development projects – employees, communities, customers, partners, and owners now have urgent, rapidly evolving needs that should be fully understood and given priority. The new communication and interaction realities caused stakeholders to continuously acquire digital skills, as they have become essential tools in their everyday lives. The change for cloud base solutions and AI development, creates demand for new skills and knowledge.
- Company’s resources & Infrastructure – The operational challenges could be a focal point of disruption and innovation in every area, from servers and storage to networking and software, even if the company infrastructure is up to date and already use hybrid or multi-cloud solutions. The lack of resources or IT infrastructure could impact software projects effectively.
- Time limitations – Time is now the key. Time constraints often bring down the efficiency of development teams and lead to finished mediocre quality software products.
- Reaching customer expectations – The needs of customers have changed. It is necessary to clearly understand the underlying business concept of the various software projects and bring in the features to satisfy the growing demands of the customers.
- An inadequate pool of tech talent – Another challenge most companies face is a lack of IT talent, namely, software development and testing teams. An in-house IT team lead an isolated existence no matter how much they train.
- New issues regarding security and trust – Through the massification of various forms of data access, sharing and transaction, such as credit and debit cards, gift certificates, electronic cheques, or bank transfers, there is also the need for due diligence and cyber security. A holistic system is required to minimise risks, identify vulnerabilities, and inform how and when to respond to potential incidents. Maintaining customer data, credit card numbers, and sensitive competitive information has become an important priority.
59% |
In one report, IBM said double extortion attacks accounted for 59% of the ransomware attacks that IBM Security X-Force handled in 2021. |
Digital transformation at the business/IT interface
That takes us to the present day! Does the company’s current model have the strength to overcome the current business demands? Does the company software’s quality or reputation and developer’s talent meet new stakeholders’ expectations? Business leaders often find themselves balancing the short-term needs of some stakeholders with long-term planning for growth. That is the right time to think outside the box about the business approach to digital innovation.
How to Overcome These Challenges?
The hugeness, dynamism and high sophistication of software can be both an opportunity and a challenge. Strategically outsourced IT activities can improve a company’s technical skills realistically and improve critical strategic needs.
Benefits of IT Outsourcing
Many business leaders view outsourced IT as a true competitive advantage, as something that helps them get ahead without an upfront investment of time or money and a strategic opportunity to scale and grow.
- Match up with emerging business demands and technological trends. Let’s face it: a high-quality outsourced IT service will have the resources to start new projects promptly. It also reduces
- Time limitations by recovering capabilities that increase uptime by restoring operations quickly.
- Streamline day-to-day infrastructure management that often struggles to enhance results in a changing environment. Streamlining infrastructure operations through a highly skilled third-party talent pool reduces time-consuming management activities and gives the business the focus on those initiatives that drive value.
- A new, deeper pool of IT talent. The variety of specialized skill sets and a new way of thinking reach the fullest potential of leading platforms, accomplishing end-to-end transformation, and solving all kinds of issues, even those that might only arise occasionally.
- Reach customer expectations. The strongest pillar on which the business stands is the customers, and their expectations are increasingly more demanding. Nowadays, they expect top-notch support services from companies, and a comprehensive automation platform is a key to productivity and service consistency with management tools that improve efficiency without a pricey technology investment.
- Enhance the benefits of data “openness” with security and legal requirements. Having a quality third-party provider with deep experience in managing compliance risk and running operations through structured processes and compliance procedures will increase protection, ensuring that patches and updates are applied quickly. In addition, all the infrastructures will be kept up to date, and automatic software updates roll out as soon they are available.
What Are Some Most Common Outsourcing Business Models?
There are a variety of outsourcing models that can be tailored to each company’s particular needs. There are eight core standard outsourcing business models:
Location-based Outsourcing Business Models.
- Onshore Model – In this model, the external service provider is in the same country as the company that outsources its operations. The advantage is to get skilled services in complex areas such as cost-sensitive IT or BPO service industry models.
- Offshoring Model – Historically, this is one of the most known business models, where the outsourced company is in a remote location or area. The main advantage is to have highly skilled and low-cost labour, but the geographical boundaries may give rise to some disadvantages such as language barriers, cultural differences, time zones and other location-specific risks, like regulatory limitations.
- Nearshore Model – Like Offshoring, Nearshoring means outsourcing to a service provider in a different but nearby country. This is beneficial because nearshore developers collaborate tightly with company inhouse staff in real time, increasing the company’s access to a larger and more diverse pool of IT talent and reduce regulatory constraints.
Relationship-based Outsourcing Business Models
- Dedicated Team Model – This model is a common approach in large-scale projects or when it is necessary to fully redesign a project and companies lack the necessary resources in-house. Hiring highly skilled professionals on a temporary basis will make the project more time-efficient, saving money for the company.
- Team Extension – This model typically offers a more affordable option for small businesses or special projects to meet specific standards and goals over time by hiring a provider to supplement the company’s workforce. It offers an advantage to meeting company deadlines for permanent or temporary needs without the resources to attract and hire talented employees in-house.
- Task-based Model – Also known as the project-based model, it is a useful and cost-effective option for one-off and pilot projects such as software development, website design, and product engineering. It involves hiring an outsourcing provider to develop and complete specific tasks at a certain hourly rate.
Knowledge-based Outsourcing Business Models
- Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) – This is a type of outsourcing where an outsourcing company is hired to perform one or more business functions in a company, such as IT, customer service, or accounting, with the aim of improving efficiency. Task-shifting typically involves contracting out a specific complete process to ensure greater efficiency, process standardisation and scale economies.
- Knowledge Process Outsourcing (KPO) – In this model, the company acquires specific services from a specialist third-party in a particular knowledge-related task. Market studies, complex projects or specific services are outsourced to an expert company that carries out the process of collecting, managing, analysing, and providing objective knowledge.
Pricing Outsourcing Business Models
- Time-and-material Model (T&M) – In this model, the company acquires specific services from a specialist third-party in a particular knowledge-related task. Market studies, complex projects or specific services are outsourced to an expert company that carries out the process of collecting, managing, analysing, and providing objective knowledge.
- Fixed-price Model (FP) – In this model, the company establishes a fixed price for a clearly defined scope of work over a certain period, such as managing servers, developing applications or monitoring networks. This model is appropriate for long-term projects when the criteria are well defined, with no prospect of incurring variable costs during software development.
- Incentive-based Model – This model allows the outsourcer to earn further payments or rewards based on the performance specification. That is a creative fee structure bringing together the two models described above and aims to align the outsourced supplier between prioritised business objectives.
Strategic outsourcing: Where does the CEO fit in?
In the right context, outsourcing can be a great way for business owners to improve efficiency and strengthen their company’s bottom line. Even if the business is already established or even if it is a new business, outsourcing technical skills, can free up companies to focus on their strengths, allowing internal staff to concentrate on their core tasks and future strategy. The CEO has an important role in outsourcing deployment, reshaping the company’s approaches to risk.
Vision and strategy
As CEO, you are advised to put your IT outsourcing into a broader strategic perspective.
How important is IT to the organisation today, and how does it fit into your future vision and mission?
How well does IT support your current business processes, and how adequate is it suited to handle the potential complexity of change?
By asking these questions, you will be in an advantageous position to judge what should remain in-house and what can be fulfilled through outsourcing. Various methods are available to help you prepare your strategy for the business and back-end IT landscape. Getting advice on these issues from external experts without directly committing to outsourcing can be one way to understand how best to leverage the company’s strategic objectives.
Commitment to change
The successful digital transformation of a company does not depend only on the CEO, although the CEO should have a good understanding of the digital changes his company faces, how they affect its business model and, at the same time, how to create a business environment that makes room for technological experimentation and new types of cooperation. With technological advances comes progress and change, and the aim is to effectively implement strategic objectives in an efficient and cost-effective manner, always keeping in mind the strategic priorities, including budgetary concerns.
And it is possible to do this even in an operational environment. For this reason, blueprints are developed to meet transition needs and interim temporary states that facilitate the process change. Interactive management of the overall process is vital in this context, including reporting, monitoring and adjustment, as well as financial management, resource planning and risk management.
This is a major business and strategic decision, and the CEO’s commitment is crucial to ensure good communication between the board, business operations, and the outsourcer, ensuring the company’s overall growth.
Focus on what you do best and outsource IT to specialists!
